Uric acid is the final product of purine metabolism in the human body, primarily excreted through the kidneys into urine. In general, the amount of uric acid produced in the body equals the amount excreted, maintaining a balance.
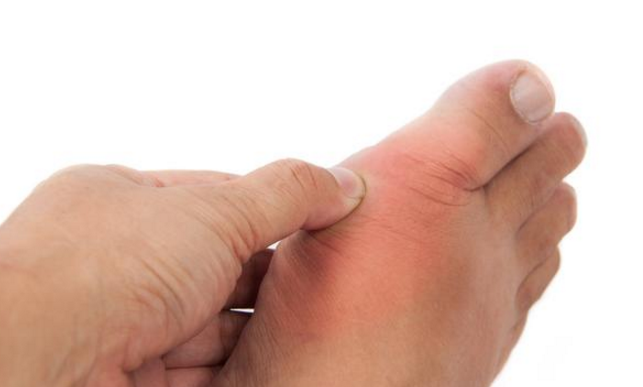
When the uric acid level exceeds the excretion capacity, it enters the bloodstream. Once the blood uric acid concentration is too high, it can deposit in various body tissues, leading to symptoms such as joint pain, gout (swollen, hot, painful joints, especially in the fingers and toes), dry mouth, body swelling, and abnormal urination.