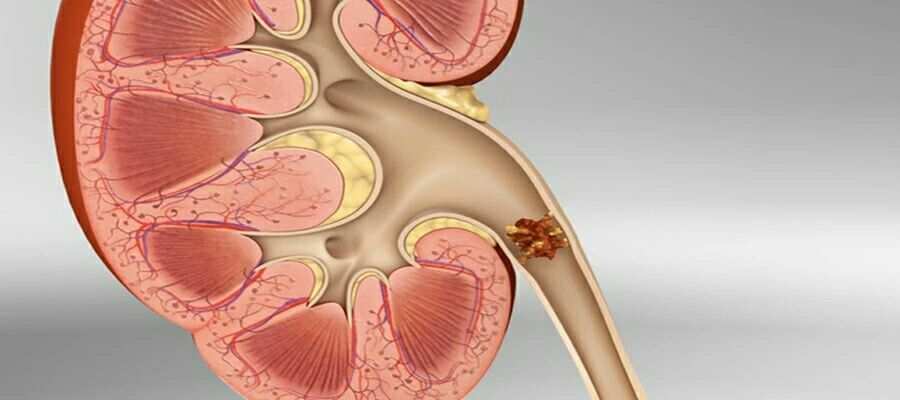
A family history of kidney stones can significantly increase an individual's susceptibility to developing them. Genetic factors can influence the way the body processes and excretes substances that may contribute to stone formation.
Certain medical conditions and metabolic disorders can predispose individuals to kidney stone formation:
Hyperparathyroidism: Overactivity of the parathyroid glands can lead to increased calcium levels in the blood and urine.
Gout: Elevated levels of uric acid in the blood can crystallize and form uric acid stones.
Cystinuria: A genetic disorder that causes the kidneys to excrete too much of certain amino acids, leading to cystine stones.
Renal Tubular Acidosis: A condition where the kidneys are unable to properly acidify the urine, increasing the risk of calcium phosphate stones.