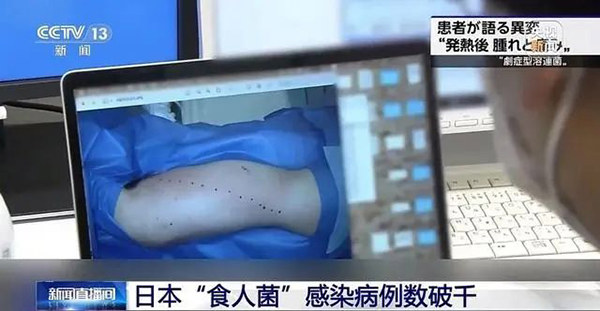
However, in addition to acute inflammation, there is also chronic inflammation. If the immune response to tissue damage becomes uncontrolled, chronic inflammation may occur, potentially leading to the development of cancer. Chronic inflammation continually progresses in the body, causing changes such as DNA mutations and genetic damage accumulation, which may induce the formation of cancer-initiating cells.
Furthermore, cytokines produced during the inflammatory response can accelerate the growth rate and quantity of cancer cells, thus promoting the occurrence of cell carcinogenesis.
However, overall, inflammation is a defensive mechanism and has a protective effect. Only persistent, unregulated chronic inflammation is likely to develop into cancer.
Four Types of Inflammations