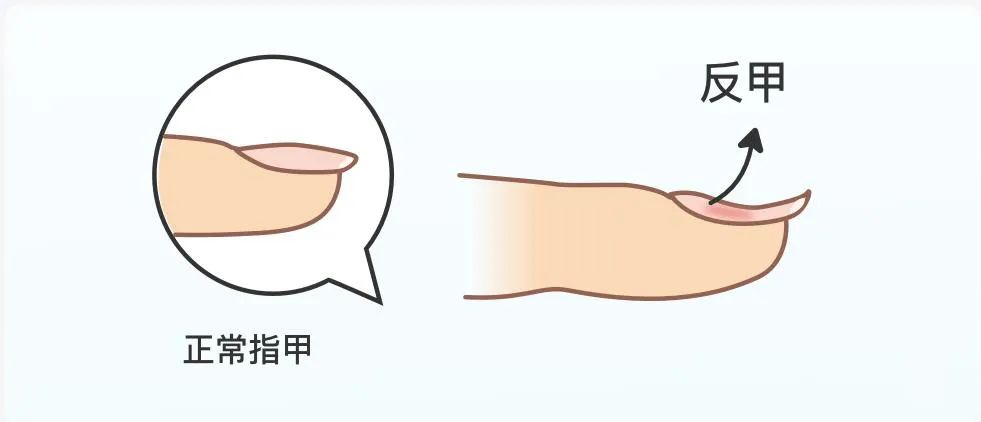
2. Bedtime:
Going to bed too late can also contribute to increased blood sugar. A study involving 953 healthy adults recorded their sleep patterns and postprandial blood sugar levels for two weeks. The findings revealed that going to bed late on one night was associated with higher postprandial blood sugar levels the next day.
Staying up late reduces the liver's conversion and storage functions, causing many carbohydrates from food to remain in the bloodstream as glucose, leading to elevated blood sugar. It is advisable for individuals with high blood sugar to aim for a regular sleep schedule and try to sleep before 11 PM.