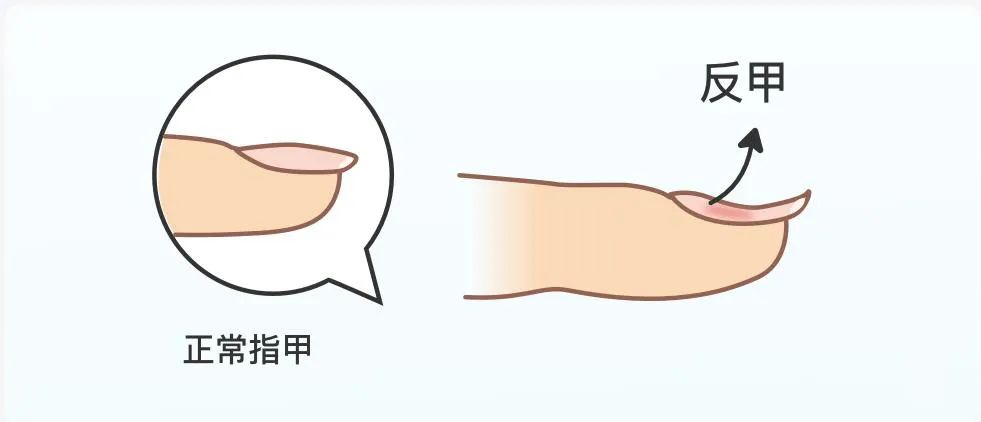
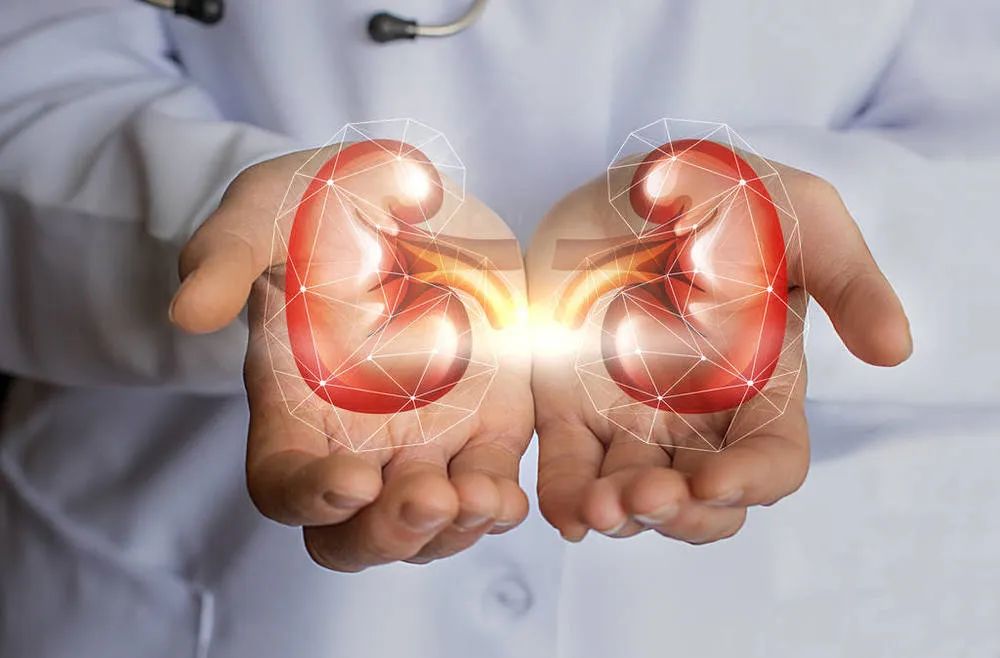
Hyperuricemia is often associated with chronic urate nephropathy, kidney stones, acute uric acid nephropathy, and severe impairment of kidney function, which may progress to kidney failure.
Additionally, high uric acid levels can lead to kidney fibrosis, accelerating the process of kidney sclerosis.
5. Joints
When uric acid enters the bloodstream and reaches various parts of the body, it tends to form urate crystals, which can deposit in joints and surrounding tissues, causing acute inflammation and pain in the cartilage and synovial tissues. Gout is a typical example of this condition, which can severely affect limb movement.