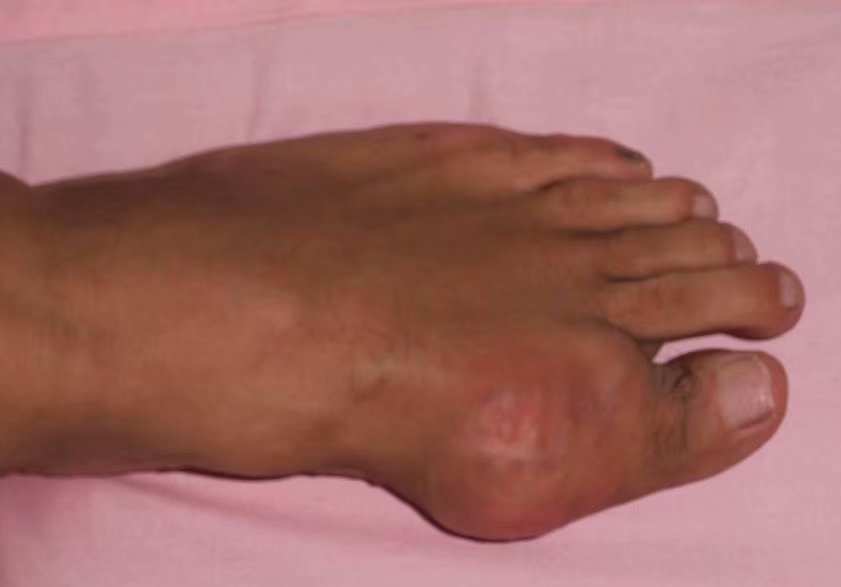
Some medications can increase uric acid levels or interfere with its excretion, contributing to gout. These include diuretics (water pills), low-dose aspirin, and medications used in the treatment of hypertension and heart disease.
Beer and other types of alcohol, especially when consumed in excess, can raise uric acid levels and trigger gout attacks. Beer is particularly linked to gout due to its high purine content.
Gout is more common in men than in women, especially between the ages of 30 and 50. Women's risk of developing gout increases after menopause.