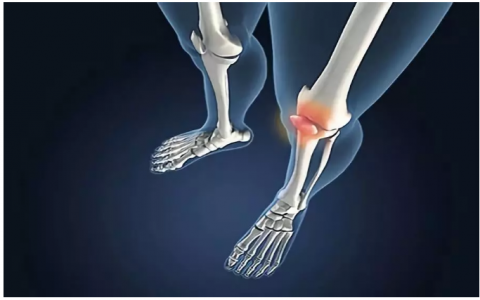
Gout tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition to the condition. Some people inherit genes that affect the way their bodies process and eliminate uric acid, making them more susceptible to gout.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of gout as excess body weight can lead to higher uric acid levels.
High Blood Pressure: Hypertension and gout are often linked, possibly due to shared risk factors such as obesity and diet.
Diabetes: People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing gout, possibly due to insulin resistance affecting uric acid excretion.
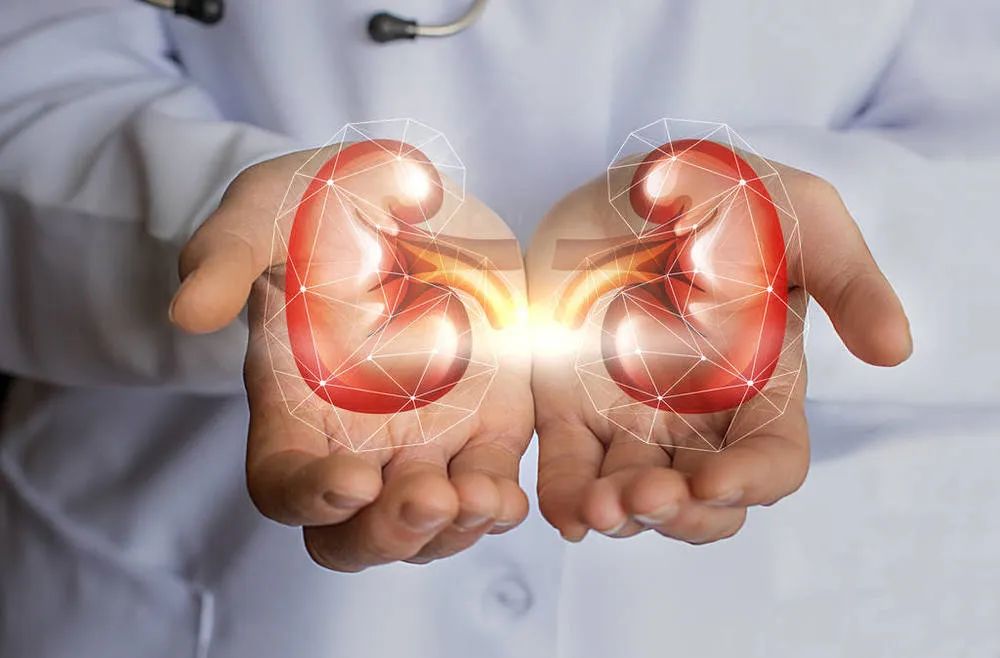
Kidney Disease: Impaired kidney function can prevent the efficient elimination of uric acid, leading to its buildup in the blood.